 For half an hour or so I felt I was back at University at Software 2007 – in Professor Hasso Plattner’s class. That’s because his keynote was a compressed version of his recent SAPPHIRE 07 speech, which in turn was an “offsite class” for his Stanford students – literally so, he flew the entire class out to Atlanta. To make his point, he used the blackboard-metaphor, with chalked handwriting (and dressed in matching black
For half an hour or so I felt I was back at University at Software 2007 – in Professor Hasso Plattner’s class. That’s because his keynote was a compressed version of his recent SAPPHIRE 07 speech, which in turn was an “offsite class” for his Stanford students – literally so, he flew the entire class out to Atlanta. To make his point, he used the blackboard-metaphor, with chalked handwriting (and dressed in matching black ).
).
I don’t normally enjoy keynotes, but found this one fascinating: it was about a lot more than most in the audience thinks – more on this later…
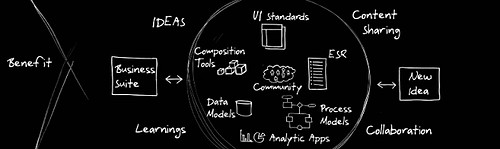
The “lecture” was about his New Idea for enterprise software – more than an idea, it started as a side-project about 5 years ago, then about 3 years ago they realized they can’t do it with one codebase.. so it became a completely separate system from SAP’s current business suite. They kept the project secret as long as they could, but this year they started to talk about it: it’s code-named A1S, and currently 3000 people are working on it (For comparison, Salesforce.com has less than 200 engineers). It will be On-Demand, and not a point-solution, but a full-featured, integrated business solution, as one would expect from SAP.

Some of my raw notes on the key concepts:
- On-demand: Google, Salesforce.com showed it works. Time now for the whole enterprise to run in the cloud. Very small footprint at customer.
- New markets: small business customers.
- Key difference: user-centric design. Iteration, version 7 of user interface already, it will be 8 or 9 before it launches. Every single functions delivered either by browser or smart client. They look 100% identical. Office (MS) client, Mobile, too.
- Separation of UI, App, Db – physical sep, multiple UI’s for same App. Front ends very specific to industries. Portal based. Company, departmental portal. User roles. Multiple workplaces. In smaller companies users have multiple workplaces. High degree of personalization.
- Event driven approach. Model based system. Instead of exposing source code, expose the model. Not just documentation, active models. Change system behavior through models. Very different from SAP’s original table-based customization. Completely open to access by/ to other system. 2500+ service interfaces exposed.
- The future of software design will be driven by community. SDN 750K members, 4000 posts per day. We’ll have hundreds of thousands of apps from the community. Blogs, Wikis, Youtube.
- In-memory databases. Test: 5years accounting, 36 million line items. 20G in file 1.1G compressed in memory. Any question asked > 1.1sec. There is no relational database anymore. Database can be split over multiple computers. Finally information will be in the user’s fingertips. Google-speed for all Enterprise information. Analytics first, eventually everything in memory.
For a more organized writeup, I recommend Dan Farber’s excellent summary, and for the full details watch the original SAPPHIRE 07 Keynote (after a bit of salesy intro).
As it became obvious during the post-keynote private press/blogger discussion, most in the room thought Plattner was talking about the mysterious A1S, SAP’s yet-to-be-seen On-Demand SMB offering – although he made it clear he intentionally never used the A1S moniker. I think what we heard was a lot more – but to understand it, one has understand Hasso Plattner himself. No matter how his formal position changed, the last active SAP Founder has always been the Technology Visionary behind the company – the soul of SAP, it there is such a thing. He is not a product-pusher, not a marketer: he sets direction for several years ahead.
He is not a product-pusher, not a marketer: he sets direction for several years ahead.
SAP has an existing (legacy) market to protect, and they clearly don’t want the On-Demand product to cannibalize that market. But Plattner knows On-Demand is coming, and I bet the SMB space will be the test-bed to the new system eventually “growing up” to all of SAP’s market segments. Hasso Plattner gets the On-Demand religion, and when he gets a new religion, SAP typically follows. Plattner oversaw two major paradigm changes: the move from mainframe to client/server, which was entirely his baby, and the move to SOA/Netweaver, where he embraced Shai Agassi’s initiatives. The ‘New Idea” will likely be the last time Plattner turns the Mothership around. Next he will need to find “another Shai” to make sure there is a strong tech DNA in SAP’s leadership, as the Sales/Marketing types take over at the helm.

 SAP held major internal announcements and demos of its
SAP held major internal announcements and demos of its 
 24SevenOffice
24SevenOffice
 (Updated)
(Updated)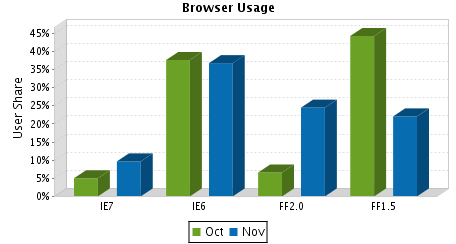
 ). Clearly, the majority of new IE7 users are not IE6 upgraders, they came from the Firefox camp.
). Clearly, the majority of new IE7 users are not IE6 upgraders, they came from the Firefox camp. Of course JotSpot had the right to do this, these were not paying customers (yet), and a beta is a beta, after all. But a beta program is a mutual effort, and especially early on requires a lot of time and effort from the customers, so it’s clear that these customers may feel let down. While most competitive migration offers are hosted solutions, it’s this specific “betrayed” group that
Of course JotSpot had the right to do this, these were not paying customers (yet), and a beta is a beta, after all. But a beta program is a mutual effort, and especially early on requires a lot of time and effort from the customers, so it’s clear that these customers may feel let down. While most competitive migration offers are hosted solutions, it’s this specific “betrayed” group that  )
)
 … but Joe Kraus, having sold Jot$pot to Google. The source was credible but of course we had already heard about a Yahoo acquisition, then eBay .. so who knows, after all.
… but Joe Kraus, having sold Jot$pot to Google. The source was credible but of course we had already heard about a Yahoo acquisition, then eBay .. so who knows, after all. – now let’s look at what Google should do with JotSpot.
– now let’s look at what Google should do with JotSpot.



Recent Comments