 Zoho is definitely getting an increasing share of attention. No wonder – they are releasing product updates at a rate others do press releases. The introduction of a single sign-on to six of their Office 2.0 applications generated quite some buzz on a normally silent weekend. TechCrunch, ZDNet, Read/Write Web, AccMan Pro, yours truly – the usual suspects, one might say, but when “good-old-fashioned” ex-Gartner Vinnie Mirchandani pays attention, you know something is brewing here.
Zoho is definitely getting an increasing share of attention. No wonder – they are releasing product updates at a rate others do press releases. The introduction of a single sign-on to six of their Office 2.0 applications generated quite some buzz on a normally silent weekend. TechCrunch, ZDNet, Read/Write Web, AccMan Pro, yours truly – the usual suspects, one might say, but when “good-old-fashioned” ex-Gartner Vinnie Mirchandani pays attention, you know something is brewing here.
Richard MacManus claims Zoho Moving Towards A Full Web Office Suite. Previously both myself and IT|Redux claimed the Zoho Suite complete. So are we there yet? Well, MS Office was called a suite long before Word, Excel or Powerpoint could really talk to each other. It was ugly, messy, lossy copy/paste for years – Zoho demonstrated a far better, seamless flow and real-time data updates between a spreadsheet, database, document and presentation at the recent IBDNetwork event, and I’m sure we’re in for some surprise at the the Office 2.0 Conference this week.
But let’s look a bit further, and we’ll find that Zoho has a few more tricks in their hat. Near-term we can expect a web-based version of Virtual Office, a communication/collaboration solution (think Outlook), which really makes the Office / Productivity suite full-rounded.
How about transactional business systems? Zoho has a CRM solution – big deal, one might say, the market is saturated with CRM solutions. However, what Zoho has here goes way beyond the scope of traditional CRM: they support Sales Order Management, Procurement, Inventory Management, Invoicing – to this ex-ERP guy it appears Zoho has the makings of a CRM+ERP solution, under the disguise of the CRM label.
Think about it. All they need is the addition Accounting, and Zoho can come up with an unparalleled Small Business Suite, which includes the productivity suite (what we now consider the Office Suite) and all process-driven, transactional systems: something like NetSuite + Microsoft, targeted for SMB’s.
(Disclaimer: although I have an advisory relationship with Zoho, the above is purely my own speculation)

 Google Groups has a
Google Groups has a 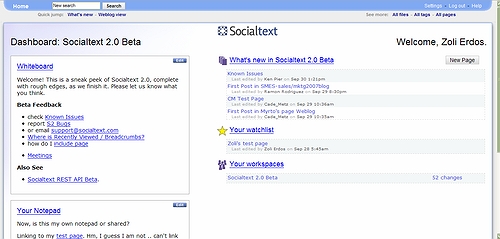
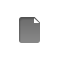
 The Home Page is of key importance in the new release: a Dashboard gives users a quick glance of a shared whiteboard, personal notepad, customizable watchlist, a listing of what’s new (i.e. recently changed pages) as well as the users active workspaces (i.e. wikis). The Home page has become the central place where you can access all extended features, like a listing of all pages, files, tags, or change settings. You can start adding information using the New Page button, which, just like the Edit and Comment buttons on all subsequent pages clearly stands out, again, passing the “blink test”. I love the new colored
The Home Page is of key importance in the new release: a Dashboard gives users a quick glance of a shared whiteboard, personal notepad, customizable watchlist, a listing of what’s new (i.e. recently changed pages) as well as the users active workspaces (i.e. wikis). The Home page has become the central place where you can access all extended features, like a listing of all pages, files, tags, or change settings. You can start adding information using the New Page button, which, just like the Edit and Comment buttons on all subsequent pages clearly stands out, again, passing the “blink test”. I love the new colored 
 We tend to think in structures, need organizing principles – there is a reason why books have a table of contents. Wikis, as unstructured as they are in “virgin state” are a good tool to create structure – our own one. The assumption of a parent-child relationship mimics our usual workflow, and it does not impose a rigid structure, since through through cross-linking we can still have alternate structures, no matter where we create a page.
We tend to think in structures, need organizing principles – there is a reason why books have a table of contents. Wikis, as unstructured as they are in “virgin state” are a good tool to create structure – our own one. The assumption of a parent-child relationship mimics our usual workflow, and it does not impose a rigid structure, since through through cross-linking we can still have alternate structures, no matter where we create a page.






Recent Comments